Google Search Results (SERPs) Explained

Ads, Snippets, Packs, Graphs & More
Google has come a long way since its founding in 1998. Traditional results gave us ten blue links but the results displayed today show a far greater depth and breadth largely as a result of increased competition from social media, a search for other channels to create more ad revenue, to answer the variety of different questions people ask, and to present the best answer possible. This, in turn, has given rise to a whole host of ways businesses can appear in Google search results.
This post will help shine a light on the most popular SERP features (Search Engine Results Page) beyond just the traditional list of blue links.
Google Searches
Here’s a starter for 10: What percentage of global market share of search traffic does Google have?
The answer? According to Net Market Share in October 2017, 80.6%.
And a bonus for another 10: How many searches are made on Google every day? One million? One billion?
In 2012 Google announced there were a whopping 3.5 billion searches per day on the platform which translated into 1.2 trillion per year! In 2016 this was estimated at beyond 2 trillion! Well, who’s counting? A trillion. Schmillion. What’s a trillion between friends?
What’s more, 15% of all searches are new, never searched before! (Interestingly, back in 2007 that figure was close to 20-25%.)
Consider as well that not everyone is searching for the same thing with the same keyword. Enter “coffee cups” and you may be looking to buy some for home, camping or your coffee shop, a cool designs, images and all sorts. How on earth do you start sorting all this data?
What you will see below therefore are the main Google SERP features (remember, Search Engine Results Pages) after 19 short years of development and several billion dollars of investment.
Bear in mind every search result Google regurgitates delivers an answer based on search intent. What is the user searching for? Not all searches will therefore, however similar they may appear, produce the same results. Is it informational, commercial or local business for example?
Note
This is not a How To guide. It doesn’t seek to explain how to appear in each of these results though it may hint at it. How Tos will come in future posts. This is a guide where all businesses and website owners can begin to understand what they can appear for.
So, without further ado, let’s dive in.
Adverts (Pay Per Click)
Google is an advertising behemoth generating over $79 billion in ad revenue in 2016!
Ads appear in two formats: text ads and product listing ads and are created, managed and placed through Google’s AdSense programme. The most common model is called Pay Per Click where, as you may have guessed, the advertiser pays every time someone clicks on the ad (as opposed to every time the ad is shown) – regardless of whether they make a purchase.
Text Ads
Text ads comprise four or more elements:
- Page title
- Google “Ad” logo identifying it as an ad
- URL
- Rich snippet, e.g. star rating
- Page meta description
Text ads can appear at the top and/or bottom of the page and are identified by the (rather small) green “Ad” sign alongside the results – the crafty folk at Google have ensured text ads look very similar to the organic results that appear further down the page.
Text ads, I believe, cause people to often mistakenly say “Business XYZ pays to be at the top of Google”. What they’re more likely saying is that they don’t recognise the ads as being ads, they don’t understand how search engines work, or they believe it’s impossible to rank high anyway as all the big industry players have taken the top spots.
Yes, you can pay to be at the top of Google if you advertise. You can be on page one tomorrow. But if you’re talking about organic search – the bulk of results that appear below the ads – then that’s a misunderstanding of how Google works. You cannot pay Google to be top of the organic search results.
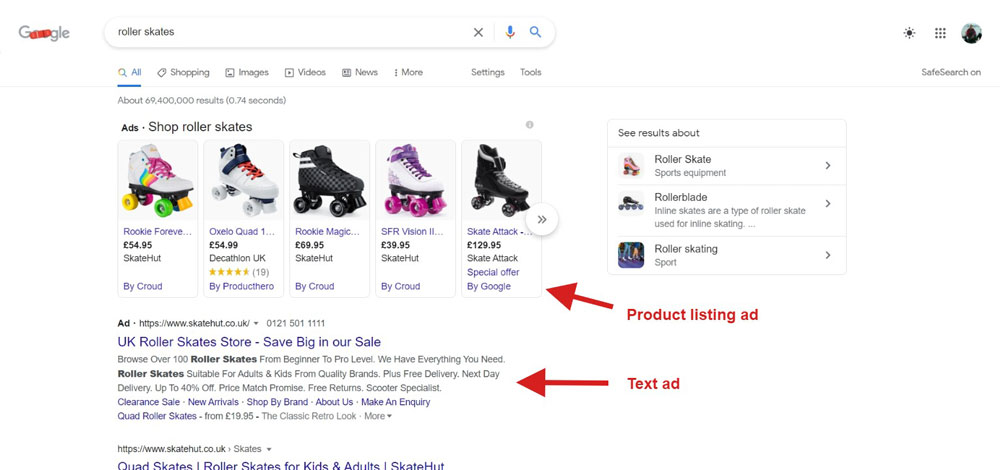
Product Listing Ads
Product listing ads comprise five elements:
- Product image
- Product name
- Product price
- Vendor
- Rich snippet, e.g. a star rating
Product listing ads are those with images and can also appear at the top of the results or down the right-hand side depending on the device used.
Googling “roller skates” illustrates the results well (not that I’m especially keen on roller skating but I have enjoyed a good roller disco in the past):
Not every search will have ads. For example, searching for “Who won the battle of Hastings” is more informational and no one is likely to bid on that keyword or phrase as it holds little commercial value. “Best dog collar” however does produce ads as there’s s high probability the user wants to buy one.
Featured Snippets
Featured snippets appear at the top of searches, in answers to questions and attribute the information to a specific site (unlike Rich Answers, below). Chances are you’ve seen it but may not know what they’re called. While you’ll be familiar with the 10 results of a search page, featured snippets appear in position zero – yes, you heard it correctly: “Position Zero”.
Featured snippets appear in 12.29% of searches and in different formats: summaries, lists, tables and videos.
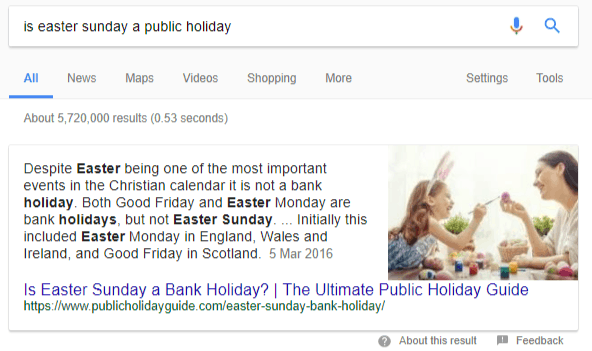
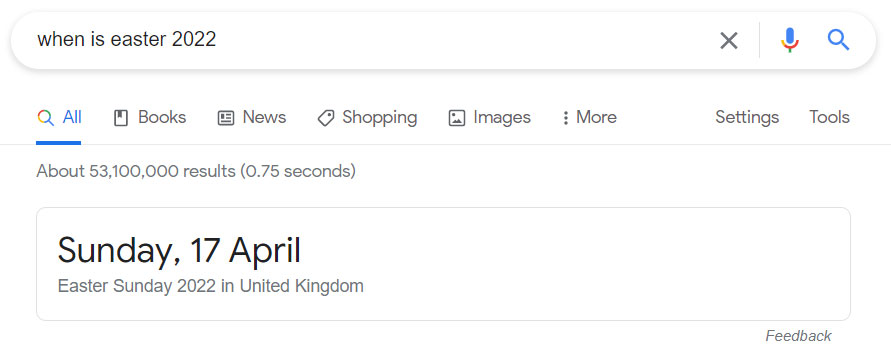
We’ve achieved position zero on several occasions with one of our websites, the Ultimate Public Holiday Guide. Googling “Is Easter Sunday a public holiday” produces a featured snippet in position zero showing:
- Text summary
- Image from the page
- Page title
- URL
Organic links appear below the featured snippet but the snippet itself does not have to be in position one, though it will most likely be on the first page. In this example the page on the Ultimate Public Holiday Guide appears in position three.
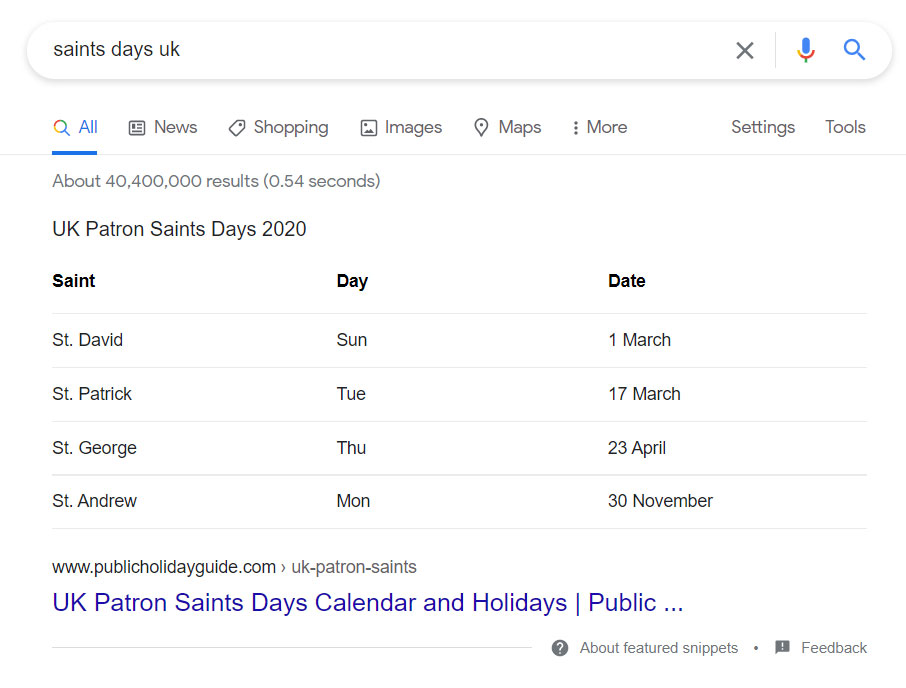
By way of another example, Googling “Saints days UK” shows a table:
SEO Note
The Guide is a relatively small site but beats the likes of Wikipedia (#1), Time and Date (#6), the Church of England (#7), the BBC (#8) and the Catholic Church (#10) to the top of the results – long may it last – showing that smaller sites can indeed top the Google rankings.
Search Engine Optimisation Training
Get found on Google
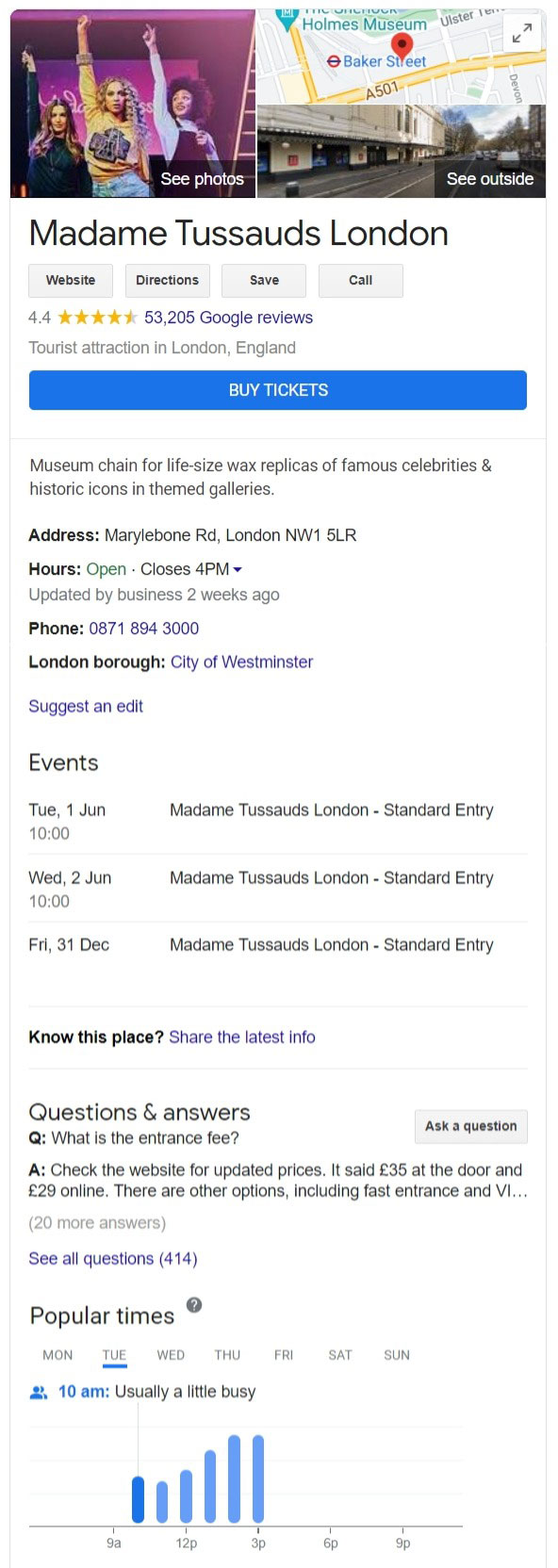
Google My Business
This is one we see many businesses fail at. We’ll devote considerable time and attention to Google My Business in later posts but suffice to say this is a free Google service that validates and indexes your business. This is the entry you see on the right-hand side of a desktop search and in a slimmed down version on mobile.
It allows you to enter your opening times, address, images, logos, allows people to review you (hint, hint) and will literally put you on the (Google) map. The only reason a business wouldn’t do this is that they don’t know about it. It is especially important for local businesses.
Rich Snippets
Rich snippets enhance listings with reviews, ratings, videos and images. Adding structured markup to your site helps generate these snippets but it’s entirely up to Google as to whether they’ll be displayed or not.
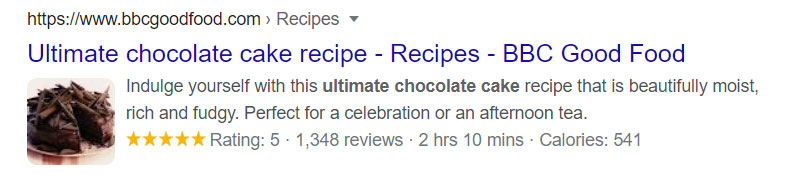
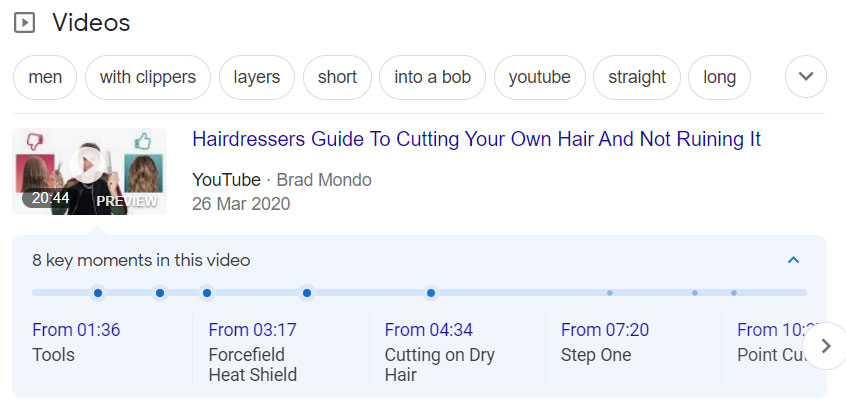
Two searches close to my heart produce rich snippets: “Samsung Galaxy S8” and “chocolate cake”. Another, “How to cut your hair long bob”, isn’t one I generally Google but you get the gist.
Knowledge Graph
Knowledge Graph was launched in 2012 as a way to better connect people, places and brands alongside traditional search results. Don’t be fooled: it’s less of a graph and more of an interconnected web of facts, figures, images and assets. Music, famous actors, your business listing. Results can be compiled into a carousel or displayed in their own box.
Rich Answers
According to Search Engine Journal “Rich Answers, also known as Instant Answers (formerly Quick Answers) are answered by Google, instantly, without credit to the site.”
You may ask “Who is president of India” or “When is Black Friday”. The important thing to note is that no site attribution is provided. Answers are generally deemed common knowledge.
Search Engine Optimisation Training
Get found on Google
Organic Search Results
Organic results are the holy grail of online search and consist of three or more elements:
- Page title
- URL
- Meta description
- Site links or rich snippets, e.g. event details
Organic results are what people normally associate with search results – the 10 blue links – which makes being on page one so essential to your organic search engine success.
Sitelinks often appear directly below a result. Webmasters and business owners can’t force sitelinks to appear as Google “only show[s] sitelinks for results when we think they’ll be useful to the user” and in any case they often appear for searches relating to very specific sites. However, there are certain things you can do to up the ante but that’s content for another time.
Appearing at the top of results is the realm of search engine optimisation. You cannot pay Google to be at the top and even with superb content you may not be on page one, but it goes without saying that the higher your website appears in a search engine the more clicks you’ll get.
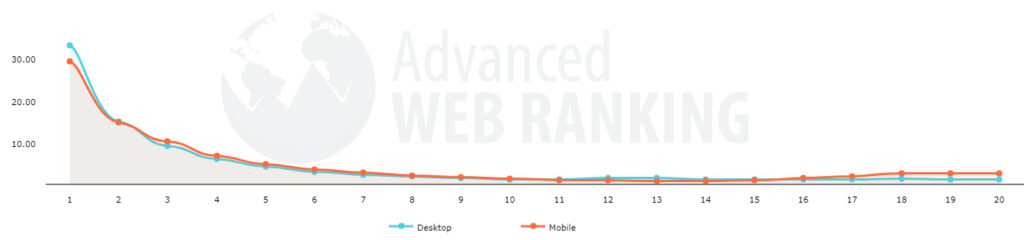
Click through rates for the UK in April 2021 according to Advanced Web Ranking are illustrated below.
Autocomplete and People Also Asked
Given the vast amount of data Google sorts it’s likely they don’t always get it right. Autocomplete helps address this.
Conspiracy theorists might say Google is trying to shoehorn steer you into conducting the most politically correct searches but with 15% of searches being entirely new … that’s one helluva lot of data to crunch. Wouldn’t it just be easier to make some suggestions?
Half way down the search results also appears other search suggestions called People Also Asked.
SEO Note
People Also Ask is another way to uncover great ideas for your content strategy. If you’re finding keywords and topics are too competitive to rank for or stuck for ideas take a look at the PAA section, should they appear, and see if you can provide better answers.
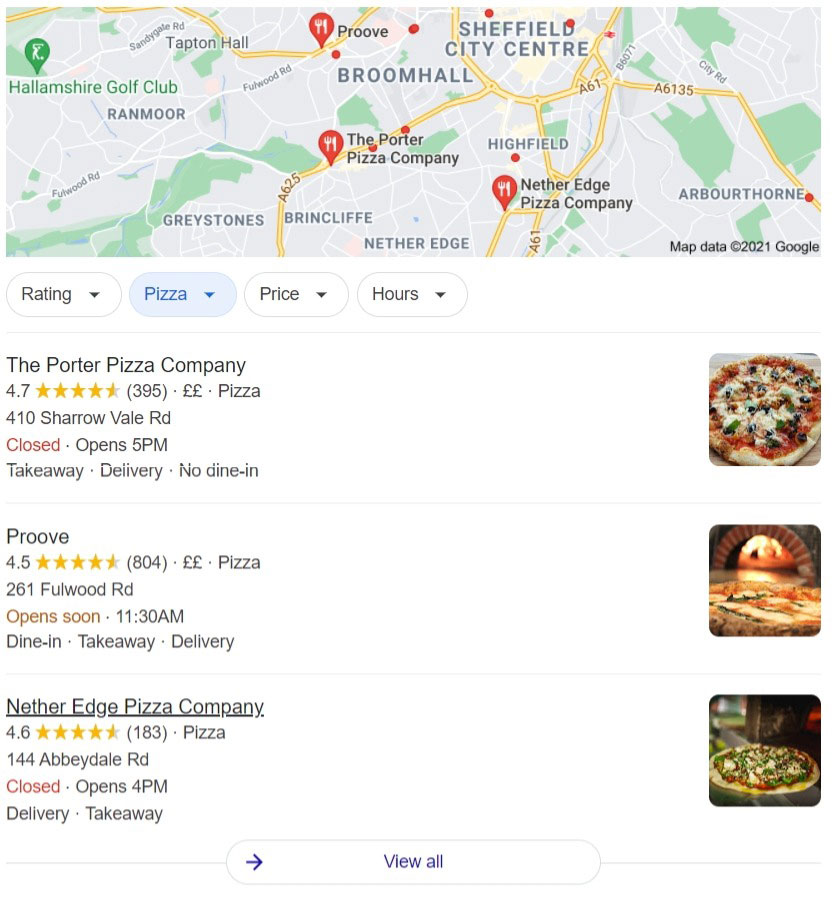
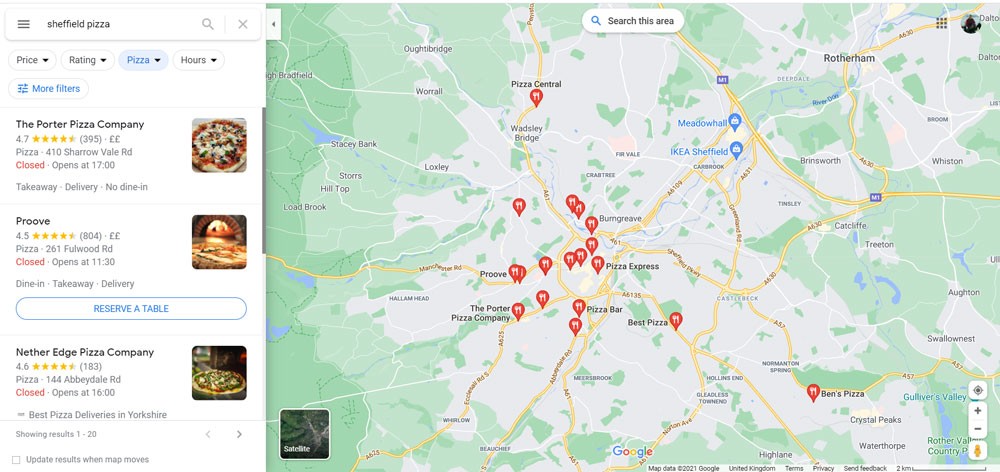
Local Pack
The Local Pack shows a map with three business locations below. It relates specifically to local businesses. Searches often include a geographic location or a location identifier of some sort, e.g. “Computer repair Basingstoke”, but if you’re on a mobile or logged into Google then results can geolocate you anyway and provide the best results.
So, if I Google “Sheffield pizza places” the following results appear and clicking on an individual result produces yet more information on Google Maps:
Appearing in the local pack is very much a part of a specific part of search engine optimisation called Local SEO and requires you to be located geographically near to the named location or geolocated user. For example, if you’re a Portsmouth based piano teacher you won’t appear in a Newcastle local pack listing.
Localised listings (the normal organic results but based on a geographic search) on the other hand aren’t quite so specific and you can manipulate appear in results even if you’re 100 miles away by simply having a well optimised page and an authoritative website.
Ranking in the local pack involves creating a strong Google My Business profile with lots of reviews, a consistent name, address and phone number wherever your website is listed (or NAP as it’s known in the trade), getting citations from online directories, creating the right content for what you want to be known for, and being recognised as a quality local provider.
As above, Proove pizza has 160 Google reviews and averages 4.5/5 stars – double the number of reviews Pizza Hut and Pizza Express have.
Search Engine Optimisation Training
Get found with our one-day course
Image Pack
The image pack is self-explanatory. You’ll need to be pretty authoritative in you field to appear here but you can improve your lot by having:
- Descriptive file names
- Descriptive alt text
- Descriptive URL
- Small enough file size
- Descriptive title
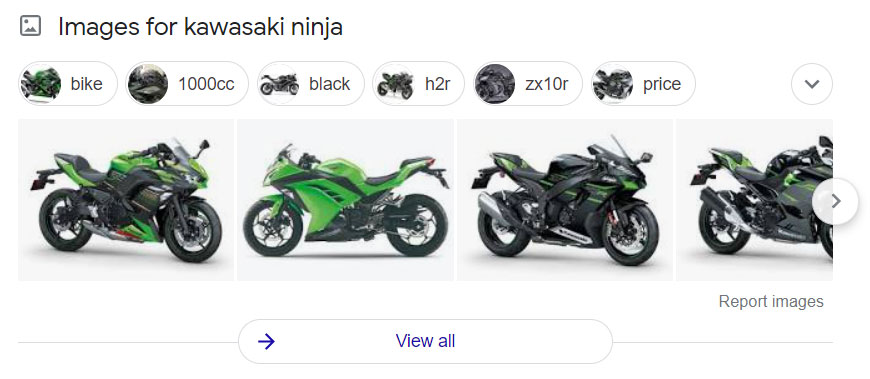
Searching for the motorbike “Kawasaki Ninja” produces some awesome images of said bikes:
News Box
The News Box is an interesting feature as it’s very much wrapped up with Accelerated Mobile Pages or AMP – a certain type of page markup free from much of the design bloat of a normal web page and which load rapidly fast. (Think of the rise of mobile use, poor data connections and download speeds.) More about AMP in another post.
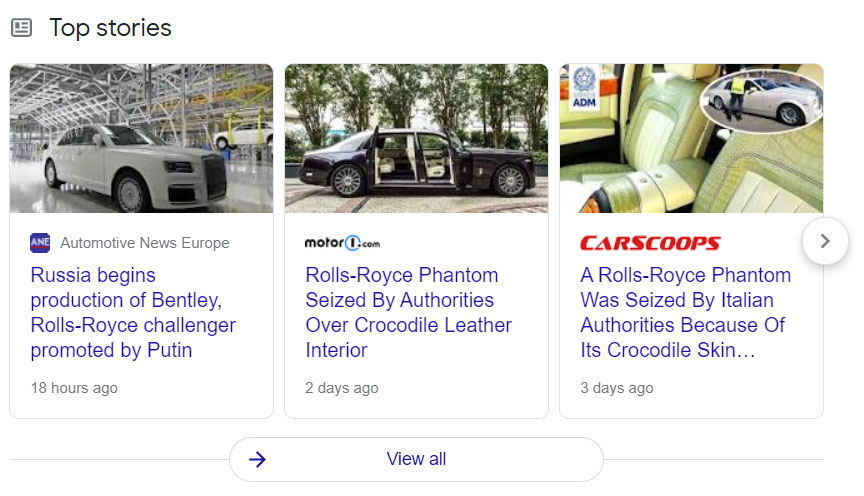
Clearly, entries must be newsworthy so it’s particularly relevant for up to the minute stories. Searching for “Bugatti Veyron” produces Top Stories (as well as images and videos) as Google tries to cover several interests:
Other Ways to Appear in Google Search
There are other ways to appear in Google search results but they’re often variations on the above. Recipes, for example, can be rich snippets if they include a star rating or video, or a featured snippet. In-depth articles appear for more investigative, academic work. Films and music can appear as a carousel as part of the Knowledge Graph.
Sporting and cinema searches produce a multitude of results including a fixtures, Top Stories, tweets, current movies, showtimes and Google My Business Listings.
Conclusion
Google is evolving all the time but not everything it does is an out and out winner: take a look at this list and Google Authorship. Next time you search though take a moment to examine the results and ask how your business might benefit from appearing in them. Consider how these search results may apply to your business.
What’s been your experience of appearing in Google? Do you favour ads? Are you optimise to appear in the organic blue links, news, or are you a budding chef with recipes galore? Let us know below.
Search Engine Optimisation Training
Take control of your online presence